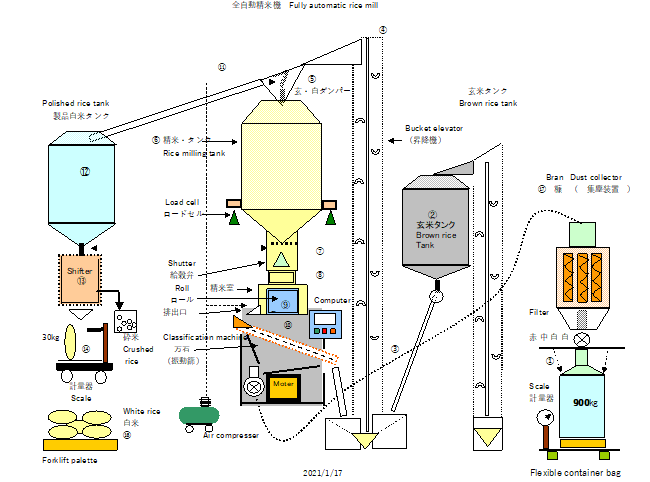
The rice milling process and the technology used in traditional Japanese sake brewing are quite unique. The outer hull, embryo, etc. are forcibly removed from the surface of the rice, leaving only the starchy interior.
The first description of how to brew sake using polished rice is written in the diary of an old monk, "Tamon-in diary". *1
Today's sake brewing is preserved from the "Moro-Haku (both white)" brewing method described in the diary.
In Moro-Haku method, 20% of the rice ingredient is accounted for koji rice, which is used to saccharify starch, and the remaining 80% is kake rice, which is saccharified by the enzymes of the koji rice and converted into alcohol.
The diary describes the brewing method in which both koji rice and kake rice are polished to produce more delicious sakes. In earlier times, only kake rice of the two types of rice was used to brew sake, called ”Kata-Haku"(one white).
*1 Tamon-in diary: A diary of stories from all over the Kinki region written by three generations of monks at Tamonin, a temple at the end of Kofukuji Temple in Nara, from 1478 to 1618.

Photo: 900kg brown rice in the flexible container on November 28, 2020

Inspection certificate of brown rice for sake brewing:
Name: Yamada-Nishiki,
Class: Extra special
Rice milling in sake brewing was put to practical use with a foot-powered "stone mill". Throughout the Edo period, "cold preparation" became established, and in the process, it became possible to obtain a large quantity of white rice by polishing rice with a water wheel powered by the flow of the river, and sake brewing took a step toward modernization. In the Meiji era, small and medium-sized breweries were established throughout the country, playing a part in tax revenue.
However, many breweries were not adjacent to rivers with adequate water and flow velocity nearby in wintertime. After gasoline engines were tested as the alternative power source, rice milling machines using electric motors eventually became widespread.
The whetstones which were sintered and shaped like a piece of Japanese chess for grinding is rotated by the motor at the center of the cylinder in the rice milling machine room, and brown rice is naturally dropped from the upper tank.
The vertical pressure due to gravity and the combined pressure pressed against the wall by centrifugal force is adjusted by the resistance plate at the outlet, and the rice is rotated vertically and horizontally to shave off the bran components from the surface of the brown rice. It is called a “vertical type rice milling machine” and has developed independently.
The evolution of whetstone, which is the most critical part of the rice mill, has a basis on the silicon carbide technology used for iron cutting and polishing at prewar shipyards.
Major rice milling machine manufacturers for brewing are Shin-Nakano Kogyo and Satake Corporation, both originate in Hiroshima Prefecture.
After the development of the rice milling machine, it has been improved, and now fully automatic computer control is installed. For the material of whetstones, Shin-Nakano Kogyo adopt artificial diamond rolls in its model: NF-20FA, and Satake Seisakusho adopt cBN “cubic Boron Nitride” in its model: EDB40A.
Both products employ artificial materials for whetstone to greatly improve the accuracy and efficiency of rice milling.
The old technology that is drawing attention recently has been put into use. That is called "flat rice milling", and it is not a traditional method of shaving brown rice to a rugby ball shape, but it is a method of effectively shaving the outer part of brown rice in which ingredients are not suitable for brewing and making the shape like "flat".
Satake corporation's EDB40A is superior for practical use of flat rice milling. Due to the shape of the roll and the size of the roll diameter, it has excellent peripheral velocity and high efficiency in rice milling.
Until around 1960, rice mills were operated at breweries nationwide. However, today, the number of breweries who operates rice milling themselves has decreased to about 100 out of the 1,200 breweries nationwide, and most of them outsource it to specialized contract rice millers for sake brewing.
The shape of the whetstone is utmost critical for improving the accuracy of rice milling.
Various shapes of whetstone have been invented, but we believe that the cone shape is the best.
At Matsumoto Brewery, we use Satake's EDB40 for in-house rice polishing. The brewery uses Yamadanishiki from Tojo Town in Hyogo Prefecture as the late rice variety for sake brewing, and Gohyakumangoku from Nanto Town in Toyama Prefecture as the early rice variety for rice milling.
This year, we milled rice 97 times from October 2nd to December 29th, with an average of 360 kg (1800-1200 kg) per milling.
The brown rice we used was 132,000 kg, the total rice polishing time was 1,710 hours, the polished white rice was 77,800 kg, and the average rice polishing rate was 58.9%. The bran produced during the rice milling process is stored in a flexible container bag.
We start the next rice milling in the afternoon. The rice milling machine operates automatically based on the preset target value. Polished white rice is classified by a sorting machine, and only complete grains are placed in bags every 30 kg (raw white rice).
After that, in preparation for the next rice milling, brown rice is put into the raw rice reserve tank through a "stone remover".
This operation is also fully automated once the brown rice in the flexible container bags has been placed in the hopper using a lift.
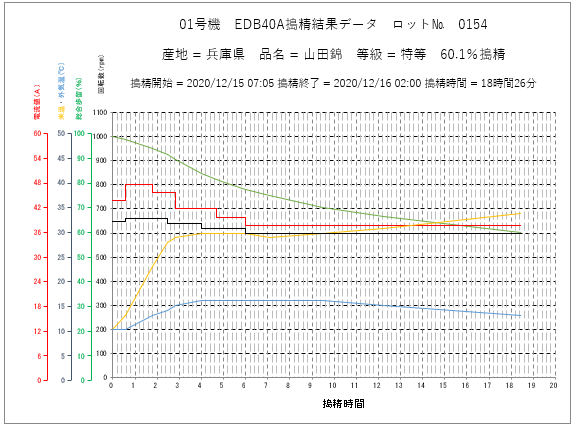
The above graph displays the rice milling data of No. 154 stored in the rice milling machine.
Along with the elapsed time of rice milling, the rice milling rate, the rice milling machine electric current value, the rice grain temperature, the rice milling room temperature, and the number of rotations of the roll are recorded. It is recorded that 1321 kg of Yamada-Nishiki was polished as polishing ratio of 60.1% in 18 hours and 26 minutes, and 793 kg of white rice was obtained, so it is possible to compare and examine the rice polishing accuracy for each lot after the rice polishing is completed.
The reason why the manual rice mill operation required a high degree of skill is that the temperature drops rapidly from daytime operation to nighttime, especially at dawn. When the temperature starts to drop, the flow rate of rice in the rice mill changes, the pressure load on the roll fluctuates irregularly, and rice crushing may occur.
Therefore, the rice milling technician had to operate the rice milling machine without sleep at night. However, with the development of a fully automatic rice mill, automatic operation was realized even at night, and the working environment for sake brewing work was greatly improved. Without the evolution of fully automatic rice milling machines, it would not have been possible to produce Junmai Ginjo Sake, which has become the mainstream today.

Photo: Appearance of rice mill, designed to match the scenery of the entire warehouse from the Takase River on December 2, 2020.
From the left, an empty bottle yard, a rice mill, a refrigerator, a product bottling yard, and boiler chimney of a "Daikoku-Kura" that is being prepared for brewing.

Photo: The building is made of reinforced laminated wood and there is no noise to the outside on January 16, 2021
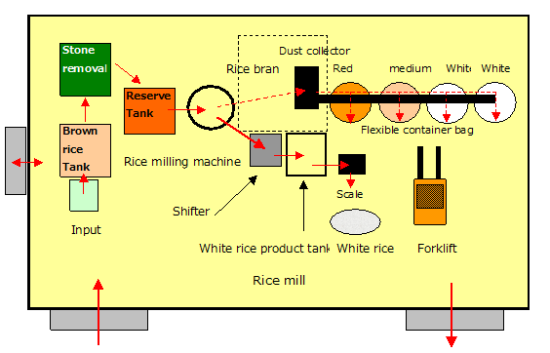
Photo: The building is made of reinforced laminated wood and there is no noise to the outside on January 16, 2021


Photo: A cBN roll (grindstone) is built in the heart of the rice mill. The diameter of the roll is 24inch.
All operations can be instructed on the operation panel on the upper side. Internal data can be retrieved via USB.
The true start of sake brewing is "steamed rice", which is made by washing, steaming, and cooling the raw material white rice. In addition to the fact that the chemical property of white rice is important, the advantage of being a "grain" that guarantees the physical property of rice is "polished white rice" produced by a “rice mill machine”, and it is the most important true raw material. However, it is unfortunately the background work with the least light of day these days.
COLUMNEssay

Essay
Scenery from the sake brewery - 007 Rice milling
Monthly photo essay on Japanese sake brewing by Mr. Keiichiro Katsuki, a Japanese sake brewing expert.
Please refer to episode 001 for more information on the author.