The principle behind the Karl Fischer method is that in a Karl Fischer reaction, water and iodine react quantitatively in a 1:1 mole ratio.
The main components of the dehydrating agent are alcohol (ROH), sulfur dioxide (SO2), and a base (RN). Within the dehydrating agent, the alcohol and sulfur dioxide react, forming sulfurous acid alkyl anions (SO3R-).
These sulfurous acid alkyl anions, which exist as [RNH]SO3R, are neutralized by the base in the dehydrating agent.
The titration reaction is shown below.
Water is consumed when [RNH]SO3R is oxidized by the iodine.
This reaction progresses quantitatively, so the amount of moisture can be determined from the amount of iodine consumed.
FAQKarl Fischer Moisture Titrators

Karl Fischer Moisture Titrators
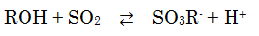
These sulfurous acid alkyl anions, which exist as [RNH]SO3R, are neutralized by the base in the dehydrating agent.
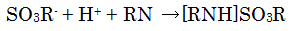
The titration reaction is shown below.
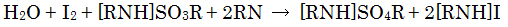
Water is consumed when [RNH]SO3R is oxidized by the iodine.
This reaction progresses quantitatively, so the amount of moisture can be determined from the amount of iodine consumed.