Principles

Refractometer / Brix meter

What is a Refractometer?
When many people hear “refractometer”, they think about the device that measures sugar concentration.
Most devices that measure sugar concentration are of this same configuration, wherein light is shined through a prism onto the test sample, and the angle of refracted light changes for each sample.
By measuring the refraction (refraction rate) of light, the refractometer can be used as a measuring device various concentrations.
Measurement Principles of KEM Refractometers
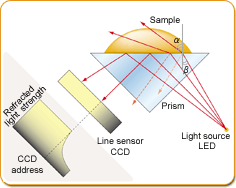
When light passes through highly refractive materials into less refractive materials, its direction changes. When angle of incidence β increases, the output angle a increases according to Snell’s Law, and when output angle a reaches 90 degrees (the critical angle), total refraction occurs on the border surface.
On an actual refractometer, the light source, prism (nD = 1.768), and line sensor CCD are positioned as pictured on the right. The strength of the refracted light is detected by the line sensor CCD, and by finding the border of “light” and “dark” above the line sensor by the CCD address, the refraction rate can be measured.
Refractometer
Refractometer Series

What are the advantages of using a refractometer?
Small amount/short time/high precision
There is no other method of refractometer measurement that combines these three features.
No difference due to human error
With analysis by hand, it is a matter of course that different measurements occur with the same sample, but when the task is left to the device, the same value results, no matter who is doing the measuring.
Automation becomes possible
With the use of such options as a multiple sample changer, the device can measure several samples on its own, after the samples have simply been lined up.
Measurement can be performed without experience or specialized skills
In analysis, there are cases in which one must have mastery of skills or years of experience. However, if one simply learns how to use the device, every person can analyze at the same level.
What kinds of analysis are performed? [Refraction rate]
Food measurement: Sugar refractometer
Fruit:
Apples, mandarin oranges, grapes, Asian pears, watermelon, cantaloupe, etc.
Vegetables:
Tomatoes, white cabbage, carrots, potatoes, etc.
Beverages:
Soft drinks, carbonated beverages, fruit beverages, etc.
Other:
Flavorings (soy sauce, ketchup), honey, fruit jam, bean jam, cream, etc.
Fat measurement
Soybean oil, sesame oil, canola oil, olive oil, etc.
Petroleum products measurement
Diesel fuel, heating oil, gasoline, etc.
Pharmaceuticals/drug measurement
Syrup, infusions, etc.
Other
Industrial chemicals, plating fluid, rinse solution, fragrance, etc.